Client
Client Usage
#test_client.py
from fastapi import FastAPI
from easyauth import get_user
from easyauth.client import EasyAuthClient
server = FastAPI()
server.auth = EasyAuthClient.create(
server,
token_server='0.0.0.0',
token_server_port=8090,
auth_secret='abcd1234',
default_permissions={'groups': ['users']}
)
# grants access to users matching default_permissions
@server.auth.get('/default')
async def default():
return f"I am default"
# grants access to only specified users
@server.auth.get('/', users=['jane'])
async def root():
return f"I am root"
# grants access to members of 'users' or 'admins' group.
@server.auth.get('/groups', groups=['users', 'admins'])
async def groups(user: get_user()):
return f"{user} is in groups"
# grants access to all members of 'users' group
# or a groups with role of 'basic' or advanced
@server.auth.get('/roles', roles=['basic', 'advanced'], groups=['users'])
async def roles():
return f"Roles and Groups"
# grants access to all members of groups with a roles granting 'BASIC_CREATE'
@server.auth.get('/actions', actions=['BASIC_CREATE'])
async def action():
return f"I am actions"
default_permissions, if unspecified
{'groups': ['administrators']}
APIRouter
FastAPI provides a APIRouter object for defining path prefixes, pre-defined dependencies, see fastapi docs for more details. EasyAuthClient can extend the main FastAPI router using the .create_api_router() method or EasyAuthAPIRouter.create().
EasyAuthAPIRouter Considerations
EasyAuthAPIRouter should be created after an EasyAuthClient or EasyAuthServer is created to ensure that the router are correctly included and visible in OpenAPI schema.
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, Depends
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
from typing import Optional
from easyauth.client import EasyAuthClient
server = FastAPI(openapi_url="/groups/openapi.json")
server.auth = EasyAuthClient.create(
server,
token_server='0.0.0.0',
token_server_port=8090,
auth_secret='abcd1234',
default_permissions={'groups': ['users']}
)
# import sub modules
from .finance import finance
from .hr import hr
from .marketing import marketing
from easyauth.router import EasyAuthAPIRouter
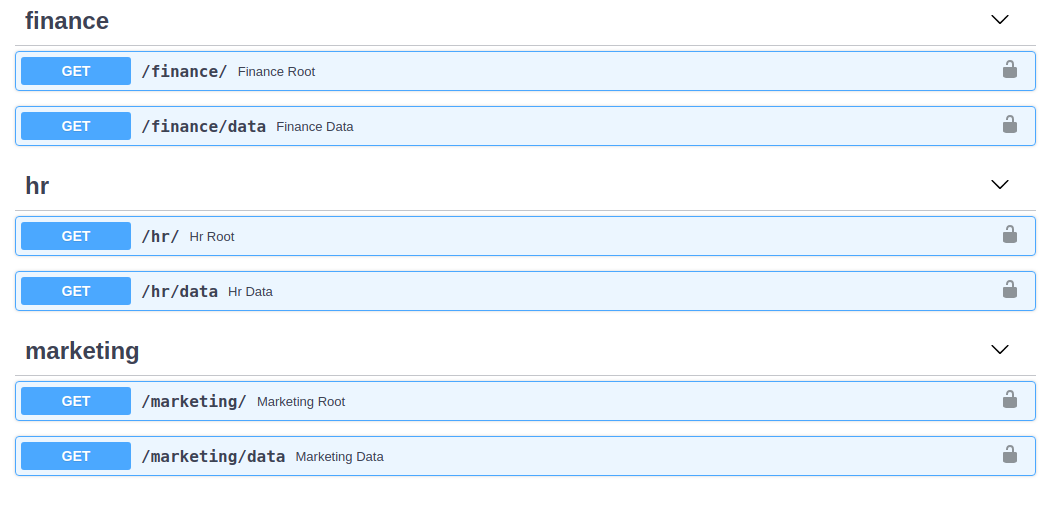
finance_router = EasyAuthAPIRouter.create(prefix='/finance', tags=['finance'])
@finance_router.get('/')
async def finance_root():
return f"fiance_root"
@finance_router.get('/data')
async def finance_data():
return f"finance_data"
Tip
EasyAuthAPIRouter.create() and server.auth.create_api_router() are wrappers around FastAPI's APIRouter, accepting and passing the same arguments, but also automatically including the router at startup.
.
├── app
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── server.py
│ └── marketing
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── marketing.py
│ └── finance
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── finance.py
│ └── hr
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── hr.py
Permissions
EasyAuth allows endpoints to be as exclusive or as inclusive as needed. Authorization is granted if user meets at least 1 condition.
@server.auth.get(
'/roles',
roles=['basic'], # OR
groups=['users'], # OR
actions=['CREATE_BASIC']
)


Cookies
EasyAuth client endpoints, decorated by the auth router, that serve HTML responses or static webcontent are provided default integrated login endpoints at /login /logout.

Note
Once logged in, the browser will contain a authenticatin cookie that matches the users token

Page Overloads
It is possible to overload the existing login, register, activation, not_found, and forbidden pages using the page specific "overloader". Just like routers, this should be done after an EasyAuthClient is created.
Danger
Consider reviewing what API's are used / required before overloading any existing page. Oauth Login scripts are not loaded into overloaded pages.
Not Found - 404
from easyauth.pages import NotFoundPage
@NotFoundPage.mark()
def custom_not_found_page():
return "Custom 404 Page"
Tip
NotFoundPage contents is wrapped in an HTMLResponse with a status_code 404.
Forbidden Page - 403
from easyauth.pages import ForbiddenPage
@ForbiddenPage.mark()
def not_allowed_page():
return "Custom 404 Page"
Login Page & 401
from easyauth.pages import LoginPage
@LoginPage.mark()
def custom_login_page():
return "Custom Login Page"
Register Page
from easyauth.pages import RegisterPage
@RegisterPage.mark()
def custom_register_page():
return "Custom Register Page"
Activation Page
from easyauth.pages import ActivationPage
@ActivationPage.mark()
def custom_activation_page():
return "Custom Login Page"
Path Overloads
The default /login and 401 redirect path can be overloaded by setting the default_login_path on EasyAuthClient.create().
server.auth = EasyAuthClient.create(
server,
token_server='0.0.0.0',
token_server_port=8090,
auth_secret='abcd1234',
default_permissions={'groups': ['users']},
default_login_path='/v1/internal/login'
)